Explore Our Health Topics
From cardiovascular conditions to holistic wellness approaches
Latest articles
Our recent publications

Bespoke psychotherapy services tailored for you in monaco
Experience psychotherapy designed exclusively for Monaco's high-achievers, combining proven methods with complete confid...

Activate your genetic potential for vibrant health and beauty
Unlocking your genetic blueprint transforms how your body builds muscle, burns fat, and maintains health. Targeted nutri...

Explore london's psychotherapy options for mental wellness
London offers a rich variety of psychotherapy options tailored to diverse mental wellness needs. From Cognitive Behaviou...

Revitalize your eyes: top tear trough treatments in london
Tired eyes and deep tear troughs can make you look exhausted and aged beyond your years. London offers a range of expert...
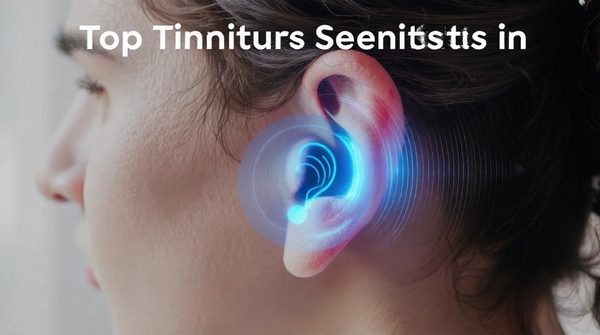
Top tinnitus specialists in london: comprehensive care solutions
...

Healing minds: discover psychotherapy in London
Finding the right psychotherapist in London can transform your mental health journey. The London Practice offers expert ...

Tear trough treatments in london: restore youthful eyes
Tear trough treatments in London offer a trusted, non-surgical solution to reduce under-eye hollows and dark circles. Us...
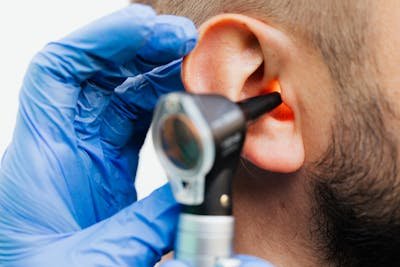
Tinnitus clinic london: expert assessment & management
Tinnitus affects many Londoners, and expert assessment is vital to managing its complex symptoms. Dedicated clinics prov...

The Impact of Obamacare Health Care on Low-Income Populations
...

Navigating your coaching journey: key insights for success
Coaching empowers individuals to reach their full potential, offering a pathway toward personal and professional growth....

Transforming anxiety: the power of hypnotherapy explained
Anxiety can be overwhelming, but hypnotherapy offers a unique approach to transform your experience. By tapping into the...

Unlocking self-awareness: a journey into psychology's depths
Self-awareness is the foundation of understanding ourselves and our place in the world. It is the ability to recognize a...

Exploring the depths of psychology: understanding yourself better
Understanding your psyche can unlock profound insights into your thoughts and emotions. This exploration connects deeply...

Apple watch: the device that saved tim cook's father's life
The Apple Watch not only revolutionizes personal health monitoring but also plays a vital role in emergencies. Tim Cook'...

Unleashing the power of hydrogen inhalers for wellness
Hydrogen inhalers are transforming wellness by harnessing the unique properties of molecular hydrogen. This innovative t...

Can Mind-Body Interventions Reduce Premature Birth in High-Risk Pregnancies?
...

How Can Digital Therapeutics Aid in the Management of Type 1 Diabetes in Children?
Type 1 Diabetes is a lifelong disease that affects millions of children globally every year. It is a condition where the...
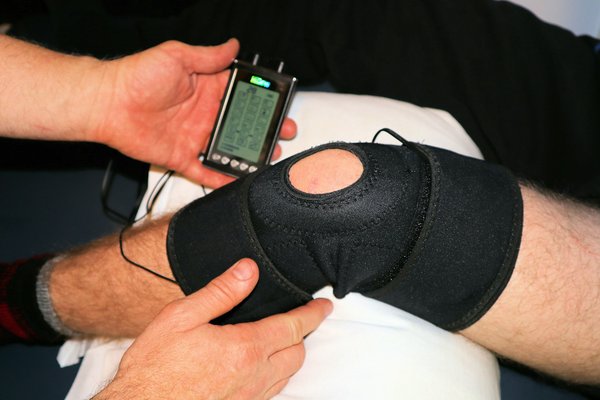
How Does Tailored Nutrient Management Affect Recovery in Athletes After Sports Injuries?
...
Does the Consumption of Antioxidant-Rich Foods Improve Longevity and Reduce the Risk of Cancer?
...

What Are the Benefits of Participating in Group Exercise Classes for Individuals with Social Anxiety?
Imagine the pounding of your heart as you enter an unfamiliar place, surrounded by strangers. This experience can be ext...

What Are the Impacts of Herbal Supplements on Liver Function in Adults with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition that affects a significant portion of the population worldwide....

How Does Custom Orthotic Footwear Promote Healing in Diabetic Foot Ulcers?
...

What Are the Health Benefits of Adopting a Flexitarian Diet?
As the name suggests, flexitarian combines the words 'flexible' and 'vegetarian', presenting a diet that promotes a vege...
What's the Role of High-Intensity Interval Training in Preventing Type 2 Diabetes?
...

How Can UK Pregnant Women Prepare for Postpartum Recovery During Their Third Trimester?
...

What Are the UK Guidelines for Managing Back Pain Through Prenatal Yoga?
As your body evolves during pregnancy, you may experience a certain level of discomfort. Back pain, particularly in the ...

What Are the UK's Recommendations for Pregnant Women Using Public Gym Facilities?
It's a common misconception that pregnancy means putting an automatic halt to all physically intense activities. There's...
Can UK respiratory therapists use new spirometry techniques to better manage chronic bronchitis in elderly patients?
As the health care landscape evolves, medical practitioners continually seek innovative techniques to manage various dis...
How can UK pediatric endocrinologists address growth hormone deficiencies with advanced hormone therapies?
When it comes to the health of your children, dealing with growth hormone deficiencies (GHD) can be a daunting task. As ...
What techniques can UK dietitians recommend for managing sodium intake in patients with heart failure?
...